Conveyor - Intuitive Python pipelines¶
Conveyor is a multiprocessing framework for creating intuitive data pipelines. With Conveyor, you can easily create stream-based pipelines to efficiently perform a series of operations on data, a task especially useful in the fields of machine learning and scientific computing. Creating a pipelined job is as easy as writing a function.
Why use Conveyor?¶
The answer is simple: throughput. It’s like putting a second load of laundry in the washer while a previous load is in the dryer. By breaking down a problem into smaller serial tasks, we perform the smaller tasks in parallel and increase the efficiency of whatever problem we’re trying to solve.
Installation¶
Install Conveyor with pip install parallel-conveyor.
A quick and trivial example¶
Let’s say we wanted to build a short pipeline that computed the fourth root of a number (done in two steps) and the cube of a number (in one step). In this case, we would describe this pipeline visually as such:
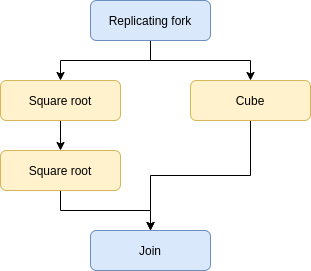 Schematic
Schematic
To express it with Conveyor, we simply build the pipeline as follows
from conveyor.pipeline import Pipeline
from conveyor.stages import Processor, Pipe, ReplicatingFork, Join
from math import sqrt
def square_root(arg):
return sqrt(arg)
def cube(arg):
return arg ** 3
with Pipeline() as pl:
# Duplicate the input
pl.add(ReplicatingFork(2))
# On first copy, compute the sqrt, on the second, the cube
pl.add(Processor(square_root), Processor(cube))
# On first copy, compute the sqrt, on the second, do nothing
pl.add(Processor(square_root), Pipe())
# Join the two data streams
pl.add(Join(2))
# Print the results
pl.add(Processor(print))
# Run the pipeline with three different inputs
pl.run([16, 3, 81])
$ python3 sample.py
2.0
1.3160740129524924
3.0
4096
27
531441